On Monday, November 7 of 2022, Lockbit hackers were supposed to publish “highly sensitive and confidential information” of Thales, a French group involved in many defense and national security programs. At 7am, the page of the darknet site shows: “All data is published”. But no file is available. 48 hours later still nothing. And finally on november 11, 4 days late, they are published. No ransom was asked.
Lockbit started their ransomware operation in 2019. They manage since to change the ransomware game and to print their name into this cybercriminal fields. So why does Lockbit is faking cyberattacks ?
 The Lockbit Ransomware-as-a-Service Game-changer
The Lockbit Ransomware-as-a-Service Game-changer
Lockbit is part of the Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) cybercriminal business. They appeared in 2019 with a unique positioning: self-spreading. It made them unique and gives a competitive edges to their affiliates intruder by automating the unauthorized access expansion tasks. Their competitors affiliates needed days or weeks to compromise a full network. With Lockbit it became a matter of minutes or hours. It is a clear competitive advantage, bringing values to their affiliates.
The second competitive advantage was the decryption support. When a company is infected, either they pay the ransom to get back their file or they loose their files. When choosing option n°1, as a victim, you expect of course to get your files after paying the ransom. If it is not the case, then you will call it a scam.
In some case the decryption process is not that easy. Because of the ransomware developer that did not put enough effort on this feature. Or because of the affiliates that lacks some technical skills. Lockbit did a wonderful job with its decryption support. Both with the decryption process and the online chat you could ping as an affiliates to get help to decrypt a victim. It puts them into the category of “reliable” and “problem solver”.
Lockbit had a clear advantage on most of the other ransomware actors: they understood it was a business. They treated their affiliates and their victims as customers. Their business-first mindset set them apart the competition and is mandatory to understand why they claim fake cyberattacks.
It is all about business … and marketing
In october 2021, Lockbit claimed to manage to break into the aeronautics giant Airbus. After investigation, it appears it was in fact an Airbus employee association. If personal data was indeed compromised, it was nowhere close to an intrusion into the main network of the company.
In january 2022, Thales’ subsidiaries Space Ops was already infected by Lockbit. The attack was real. But the cybercriminal gang exaggerated the importance of the stolen material. Instead of very highly sensitive information, it was low sensitivity data and tools stored on a server outside the defense manufacturer main network.
Cyber attack scope exaggeration, unrealistic amount of the ransom or fake compromising, Lockbit ecosystem did several false claim. It is not uncommon for hacktivist to brag about intrusion they did not perform, but unusual for a ransomware group. Unless, Lockbit is a business-first operation. And then it is more understandable how they exploit the news industry.
By claiming to achieve a huge cyber attack or asking for millions in ransom, the hacker group know they will hit the headlines. News media and blog writer will make articles rain about how incredibly dangerous the group is. And incredibly powerful their product, the ransomware-as-a-service, is. They also probably know that once a news is published, if it is incorrect, the news machinery will be reluctant to push on every channel a retraction. They will silently add an erratum on the bottom of the first article.
Intruders do also read the press. So if you are an affiliates from another RaaS provider and you struggle do decrypt or hit big target, you will be attract to pass a contract with the Lockbit developers. And became one of their affiliates.
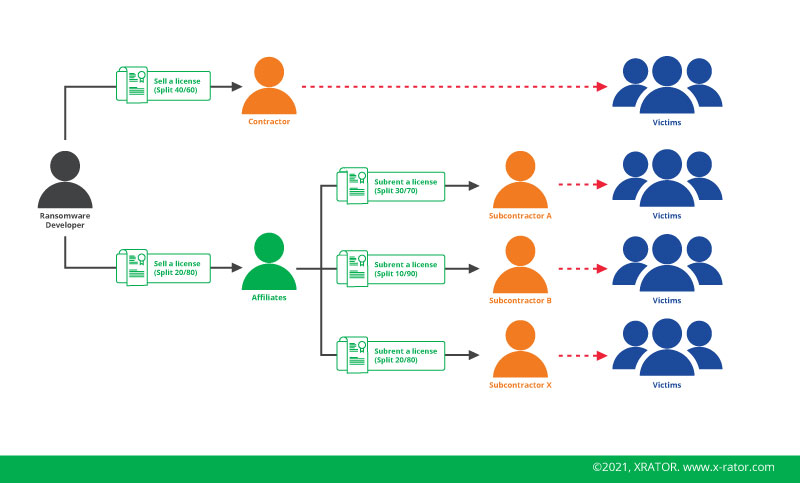
Lockbit need a constant stream of new ransomware operator as some of them get arrested by law enforcement or change for more competitive ransomware supplier.
Why Lockbit does not ask for a ransom?
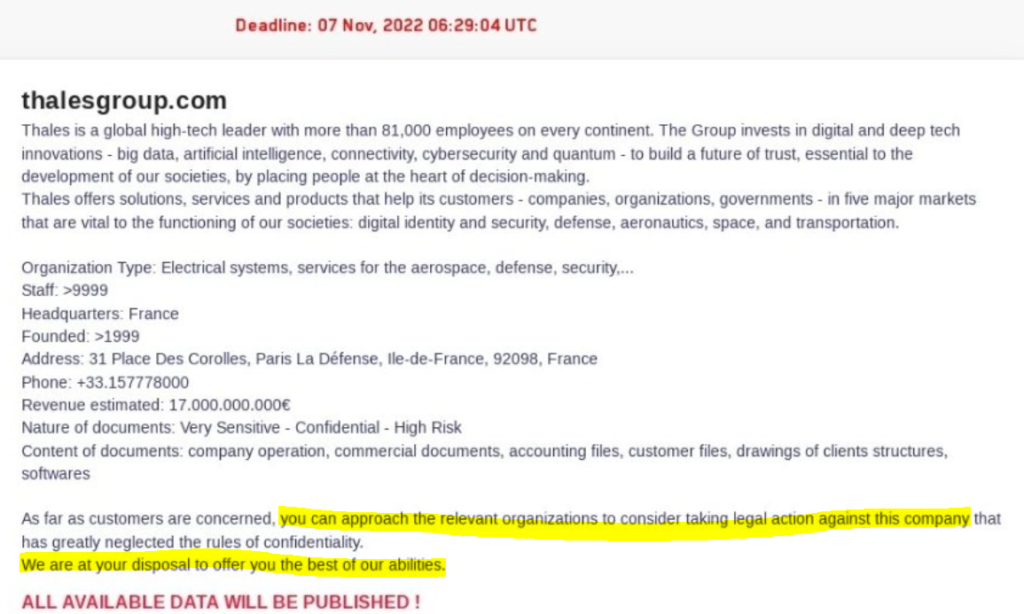
In Thales’ october 2022 case, the ransomware group do even bother to ask for a ransom. Instead the group engage customer to take legal action against the victim company for confidentiality breach. The cybercriminal group offers the best of their abilities in such a legal procedures.
This is a classical “Robin Hood” criminal behavior where the perpetrator justify its crimes by invoking the greater common good. It is also known in criminology as the Social Conflict Theory.
Lockbit demonstrated previously a great sense of business in their criminal enterprise. We can then doubt that they suddenly transform into a benevolent hacktivist group. If we consider that their stated intention are not performed in the interest of Thales’ customers, then we can advance with two non mutually exclusive hypothesis:
- PR Stunt: Lockbit is playing with the media machinery. They hack into a big sensitive company, don’t ask ransom a say they will publish for free everything. That is a first burst of articles. At the date they should have release the stolen files, nothing happened. Second firing of articles calling for scam. They finally unleashed the materials. Third waves of media coverage. We can for sure bet for at least of fourth shake when people will have review the stolen document, discussed its content and sensitivity.
- Already paid job: Lockbit was commissioned by a third party to do the job. The group had already been paid at least partially. The final motivation would be to create noise, confusion or destabilization. Thales reputation is hurt, whatever the sensitivity of the stolen material is. The sponsor could then be a competitor or a foreign state seeking for organizational gain by striking a major western defense industry player.
Conclusion
Lockbit claim fake cyberattacks because it is a very effective way to advertise their service. Ransomware developers make no money if they don’t have effective and skilled intruders and affiliates. This communication strategy allow them to catch the attention of scare resources and drive them away from the competition. More skilled affiliates means more money for the malware developers. A very sound business move. And if they can endorse the Robin Hood costume by performing sponsored operation disguised as hacktivism operation, and it is paying, then why not ?


 The Lockbit Ransomware-as-a-Service Game-changer
The Lockbit Ransomware-as-a-Service Game-changer